Source: innovationintextiles
An international research team led by scientists at The University of Texas at Dallas and Hanyang University in South Korea has developed high-tech yarns that generate electricity when they are stretched or twisted.
In a study published in the August issue of the journal Science, researchers describe twistron yarns and their possible applications, such as harvesting energy from the motion of ocean waves or from temperature fluctuations. When sewn into a shirt, these yarns served as a self-powered breathing monitor.
“The easiest way to think of twistron harvesters is, you have a piece of yarn, you stretch it, and out comes electricity,” said Dr Carter Haines BS’11, PhD’15, associate research professor in the Alan G. MacDiarmid NanoTech Institute at UT Dallas and co-lead author of the article. The article also includes researchers from South Korea, Virginia Tech, Wright-Patterson Air Force Base and China.
Yarns Based on Nanotechnology
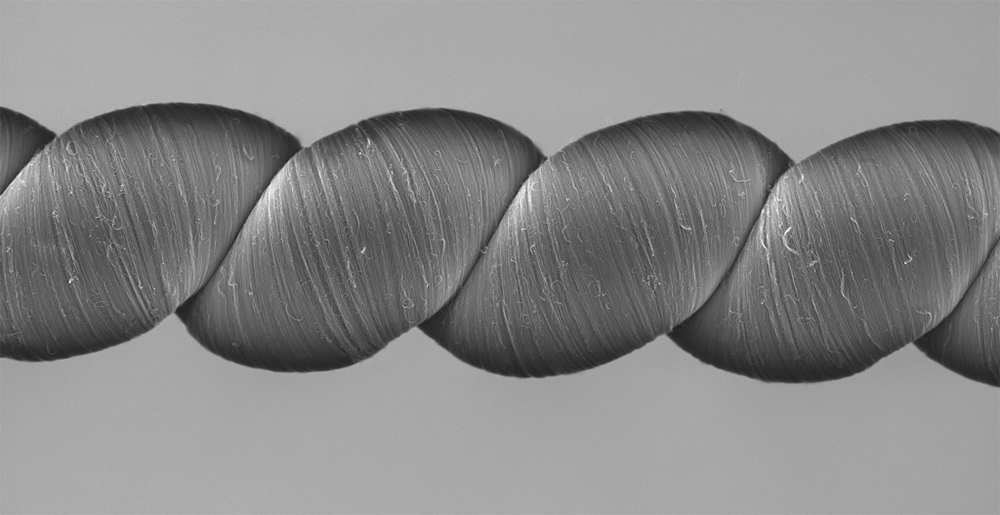
The yarns are constructed from carbon nanotubes, which are hollow cylinders of carbon 10,000 times smaller in diameter than a human hair. The researchers first twist-spun the nanotubes into high-strength, lightweight yarns. To make the yarns highly elastic, they introduced so much twist that the yarns coiled like an over-twisted rubber band.
In order to generate electricity, the yarns must be either submerged in or coated with an ionically conducting material, or electrolyte, which can be as simple as a mixture of ordinary table salt and water. “Fundamentally, these yarns are supercapacitors,” said Dr Na Li, a research scientist at the NanoTech Institute and co-lead author of the study. “In a normal capacitor, you use energy — like from a battery — to add charges to the capacitor. But in our case, when you insert the carbon nanotube yarn into an electrolyte bath, the yarns are charged by the electrolyte itself. No external battery, or voltage, is needed.”
When a harvester yarn is twisted or stretched, the volume of the carbon nanotube yarn decreases, bringing the electric charges on the yarn closer together and increasing their energy, Haines said. This increases the voltage associated with the charge stored in the yarn, enabling the harvesting of electricity.
Lab tests show potential applications
In the lab, the researchers showed that a twistron yarn weighing less than a housefly could power a small LED, which lit up each time the yarn was stretched. To show that twistrons can harvest waste thermal energy from the environment, Li connected a twistron yarn to a polymer artificial muscle that contracts and expands when heated and cooled. The twistron harvester converted the mechanical energy generated by the polymer muscle to electrical energy.
“There is a lot of interest in using waste energy to power the Internet of Things, such as arrays of distributed sensors,” said Li. “Twistron technology might be exploited for such applications where changing batteries is impractical.”
The researchers also sewed twistron harvesters into a shirt. Normal breathing stretched the yarn and generated an electrical signal, demonstrating its potential as a self-powered respiration sensor.